Authors: Tziouvaras Athanasios
Organization: Business and IoT integrated solutions
The data drift challenge: The deployment of an Artificial Intelligence (AI) workflow, especially in operational environments, poses a major challenge that is known as the data drift detection problem. Figure 1 below illustrates the standard AI workflow which is also adopted by NANCY. Data is periodically collected and packaged together to formulate a training dataset. This dataset is then forwarded to the AI model training operation which trains an AI model to fit the collected data. This process produces a trained model that can be used for inference in operational environments. The key characteristic of this process is the fact that the trained AI model is produced over a predefined dataset. As a result, a question arises regarding the quality of the model when the data distribution changes over time.
How to deal with data drift: To ensure consistent AI model quality, over large periods of time, developers have the following options: (i) Periodically re-train the AI models with newly acquired data; or (ii) Devise a mechanism that detects data distribution drifts and then, re-train the models when a significant distribution shift is identified. The first approach would ensure a decent model quality but at the cost of high energy consumption and large computational requirements. This periodic model re-training approach invokes the AI workflow in pre-defined time intervals, which translates to frequent model updates that cost energy and resources. On the other hand, the data drift detection mechanism is an approach that looks for optimal re-training periods, saves time and reduces energy consumption. This is very important since emerging technologies should take into account the need for green ICT.
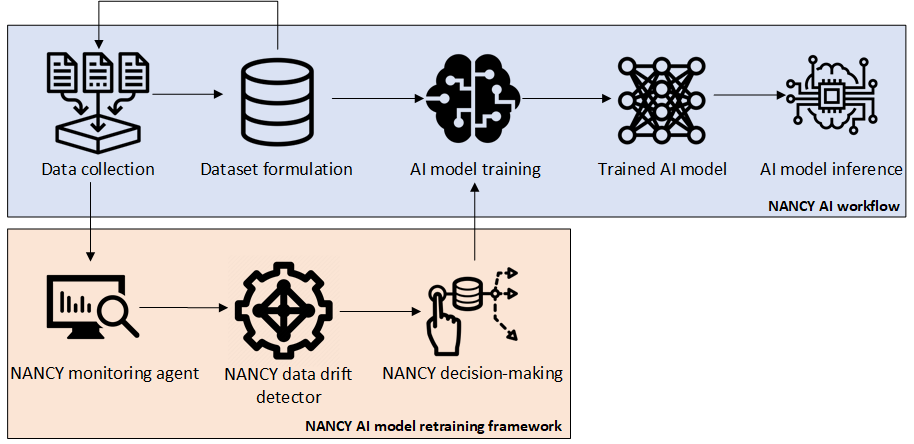
Figure 1. NANCY’s data drift detection workflow.
NANCY solution to data drift: In NANCY, we adopt and greener framework when it comes to AI model re-training operations. The adopted framework is depicted in Figure 1 and consists of three parts: (i) the monitoring agent; (ii) the data drift detector and (iii) the NANCY decision-making engine. The monitoring
agent periodically samples the data collected by the NANCY platform and feeds the detector with new information. The detector utilises a series of statistical processes and computational intelligence methods to assess whether the newly collected data depict a significant distribution shift, compared to the original data used for the AI model training process. The outputs of the detector are forwarded to a decision engine that assesses the necessity for the initiation of a model re-training operation. This operation is kickstarted when the model quality drops, due to changes in data distribution. The NANCY AI model re-training framework utilises state-of-the-art machine learning methods to find the optimal time interval for model re-training in order to co-optimise energy efficiency and model accuracy. This way NANCY reduces the computational and energy requirements of maintaining a fully operational AI pipeline.
Contributions to Green ICT initiatives: The data drift detection method developed within NANCY, is model agnostic. This means that it can be used for any type of AI pipeline ranging from image recognition, classification and segmentation to decision-making and forecasting models. This generalisability is very important since it not only increases the added value of this module but also showcases how the AI re-training operation can be used in an energy-efficient fashion within different application verticals. The design and implementation of the whole framework are inspired by the EU’s Green Deal objectives (https://commission.europa.eu/strategy-and-policy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal_en) and more specifically by the need for a Green and Digital Transformation of the EU (https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/european-green-digital-coalition).
Conclusion: NANCY addresses the need for a Green and efficient AI in Industrial and real-world environments. The deployment of the envisioned AI model retraining framework answers to day-to-day operational requirements of 5G and 6G operators, and paves the way towards a more reliable and sustainable technology ecosystem in the EU.